Kim Jong Un, the leader of North Korea, has been a figure of intense global scrutiny. Find out how his leadership style, political strategies, and impact on international relations are viewed and what he aims to achieve, plus how John Chen’s insights at johnchen.net can provide a deeper understanding of this complex world leader.
1. Who is Kim Jong Un?
Kim Jong Un is the supreme leader of North Korea, succeeding his father, Kim Jong Il, in 2011. Kim Jong Un is a North Korean political official who inherited the leadership role from his father, Kim Jong Il. His reign has been marked by a ruthless consolidation of power, a rapid advancement of North Korea’s nuclear weapons program, and significant diplomatic engagements with world leaders. Under Kim Jong Un’s leadership, North Korea has continued to be a focal point of international concern and discussion, especially in matters of security and denuclearization. Want to stay informed and delve deeper into global leadership insights? Check out johnchen.net for more in-depth analysis and leadership perspectives.
- Succession: He assumed power following his father’s death in December 2011, marking the third generation of the Kim dynasty to rule North Korea.
- Official Titles: Validated in April 2012, he acquired titles such as First Secretary of the Korean Workers’ Party, Chairman of the Central Military Commission, and Chairman of the National Defense Commission.
- Consolidation of Power: Kim’s early years were characterized by eliminating potential rivals and solidifying his control over the government and military.
2. What is Kim Jong Un’s Background and Education?
Reportedly, Kim Jong Un was educated in Gümligen, Switzerland, and later at Kim Il-Sung National War College in P’yŏngyang. Kim Jong Un reportedly attended the International School of Berne in Gümligen, Switzerland, before continuing his studies at Kim Il-Sung National War College in P’yŏngyang, North Korea, from 2002 to 2007. This educational background, combined with his family’s legacy, prepared him for leadership, blending international exposure with deep-rooted North Korean ideologies. For more insights into the backgrounds of influential leaders and their leadership styles, visit johnchen.net.
- Early Life: The youngest of Kim Jong Il’s three sons, he spent most of his life away from the public eye.
- Military Involvement: As a young adult, he accompanied his father on military inspections, gaining experience in the country’s military operations.
- Political Roles: Before becoming the supreme leader, he worked within the Korean Workers’ Party and the army’s General Political Bureau, both involved in surveillance of government officials.
3. How Did Kim Jong Un Consolidate Power?
Kim Jong Un consolidated power through purges, executions, and strategic political appointments, reinforcing his authority and eliminating potential threats. Kim Jong Un solidified his position by removing key figures who posed a threat to his leadership, including the execution of his uncle Jang Song-Thaek in 2013. These actions sent a clear message of his zero-tolerance policy toward dissent. He also strategically appointed loyalists to key positions, ensuring his policies were unchallenged. This consolidation of power was critical in enabling him to implement his vision for North Korea. Discover more about how leaders consolidate power and maintain control by exploring the resources available at johnchen.net.
- Execution of Jang Song-Thaek: In December 2013, Kim executed his uncle, accusing him of being a counter-revolutionary.
- Purges: Numerous officials who displeased the regime were reportedly executed, though accurate information from inside North Korea remained difficult to obtain.
- Strengthening Authority: By eliminating potential rivals, Kim Jong Un reinforced his position as the undisputed leader of North Korea.
4. What is the “Byungjin” Policy?
The “Byungjin” policy, adopted in 2013, emphasizes parallel development of North Korea’s economy and defense capabilities. The national strategy of byungjin, officially adopted in 2013, signifies a dual-track approach, focusing on boosting the country’s economy while simultaneously enhancing its military might. This strategy underscores Kim Jong Un’s commitment to both national security and economic prosperity, reflecting a balance between defense and development. Delve deeper into economic and defense strategies of global leaders at johnchen.net.
- Economic Development: Aims to improve the country’s economic status and living standards.
- Defense Capabilities: Focuses on advancing North Korea’s military strength, particularly its nuclear and missile programs.
- Balance: The policy seeks to balance these two critical areas to ensure the country’s stability and security.
5. How Has Kim Jong Un Advanced North Korea’s Nuclear Program?
Kim Jong Un accelerated North Korea’s nuclear weapons program significantly, conducting multiple nuclear tests and missile launches. The regime dramatically accelerated its nuclear ambitions after the first nuclear test in February 2013. By 2017, North Korea had conducted six nuclear tests, demonstrating its ability to develop and deploy nuclear weapons. Additionally, the country made significant strides in its ballistic missile technology, with missiles potentially capable of reaching the United States. Kim Jong Un’s determination to bolster North Korea’s nuclear capabilities has had a profound impact on international relations and security. Discover how leaders like Kim Jong Un impact global policies and security at johnchen.net.
- Increased Frequency of Tests: The pace of both underground nuclear detonations and long-range missile tests quickened significantly after 2013.
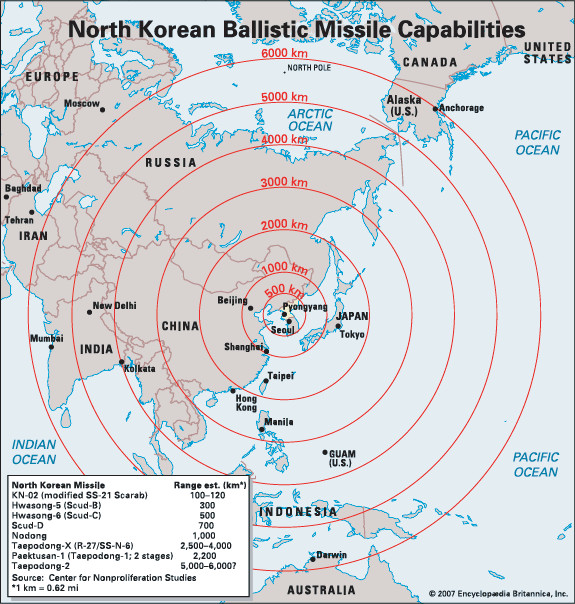 North Korean ballistic missile capabilities
North Korean ballistic missile capabilities
North Korean ballistic missile capabilities mapped for range projection from P’yŏngyang.
- ICBM Development: By 2017, North Korea claimed to have developed a nuclear device small enough to mount on an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM).
- Global Reach: With this advancement, a significant part of the mainland United States theoretically came within range of a North Korean nuclear attack.
6. What Was the War of Words Between Kim Jong Un and Donald Trump?
The exchange of insults and bombastic rhetoric between Kim Jong Un and Donald Trump escalated tensions and drew international attention. Washington and P’yŏngyang engaged in a heated exchange of insults and threats, heightening international tensions. This period was marked by aggressive rhetoric and mutual challenges, particularly regarding North Korea’s nuclear capabilities. For a comprehensive understanding of international relations and leadership strategies, explore johnchen.net.
- Insults and Rhetoric: Both leaders engaged in personal attacks and inflammatory statements, creating a highly charged atmosphere.
- Escalation of Tensions: The war of words raised concerns about potential military conflict and the stability of the Korean Peninsula.
- Unprecedented Engagement: Despite the initial hostility, the exchange eventually led to direct diplomatic engagement between the two countries.
7. What Was the Charm Offensive Initiated by Kim Jong Un?
The charm offensive involved diplomatic engagement with South Korea and the United States, signaling a potential shift in North Korea’s approach to international relations. Kim Jong Un initiated a charm offensive, marked by diplomatic engagements with South Korea and the United States, indicating a shift in North Korea’s approach to international relations. This period included historic meetings, cultural exchanges, and discussions about denuclearization. The charm offensive aimed to ease tensions, foster dialogue, and explore potential resolutions to the ongoing conflicts. Gain more insights on diplomacy and leadership strategies from johnchen.net.
- Engagement with South Korea: Kim Jong Un’s sister, Kim Yo-Jong, attended the 2018 Winter Olympics in South Korea, becoming the first member of the ruling family to visit the South since the Korean War.
Kim Jong-Un with his wife, Ri Sol-Ju, at Panmunjom in 2018.
- Invitation to the South Korean President: Yo-Jong delivered a handwritten note from her brother, inviting the South Korean president to visit him in P’yŏngyang.
- Open to Denuclearization: Kim stated he was open to discussing the elimination of North Korea’s nuclear arsenal if the United States guaranteed the security of North Korea and his regime.
8. What Was the Significance of the Summits Between Kim Jong Un and Moon Jae-In?
The summits marked the first face-to-face meetings between leaders of North and South Korea in over a decade, focusing on denuclearization and ending the Korean War. The summits between Kim Jong Un and Moon Jae-In were historic, marking the first face-to-face meetings between the leaders of North and South Korea in over a decade. These meetings focused on the denuclearization of the Korean peninsula and the possibility of concluding an armistice to officially end the Korean War. The discussions aimed to foster peace and cooperation between the two countries. Learn about effective negotiation and diplomatic strategies at johnchen.net.
- Historic Meeting: On April 27, 2018, Kim and Moon met at the “peace village” of P’anmunjŏm.
- Denuclearization Discussions: The leaders discussed the denuclearization of the Korean peninsula.
- Ending the Korean War: They explored the possibility of concluding an armistice to officially end the Korean War.
9. What Occurred at the Summits Between Kim Jong Un and Donald Trump?
Kim Jong Un and Donald Trump met for the first time in history, discussing denuclearization and U.S.–South Korea military exercises. The summits between Kim Jong Un and Donald Trump represented a significant moment in international diplomacy, as the leaders of the United States and North Korea met face-to-face for the first time in history. These meetings involved pledges towards denuclearization of the Korean peninsula and discussions about ending joint U.S.–South Korea military exercises. Despite the initial progress, the summits faced challenges and did not result in a comprehensive agreement. Gain insights into international negotiations at johnchen.net.
- First Face-to-Face Meeting: On June 12, 2018, the leaders of the United States and North Korea met in Singapore.
- Denuclearization Pledge: Kim pledged to work “toward complete denuclearization of the Korean peninsula.”
- Ending Military Exercises: Trump promised to end joint U.S.–South Korea military exercises.
10. What Challenges and Criticisms Has Kim Jong Un Faced?
Kim Jong Un’s leadership has been marked by international sanctions, human rights concerns, and skepticism regarding denuclearization efforts. Kim Jong Un’s leadership faces significant challenges and criticisms, including international sanctions due to North Korea’s nuclear program, persistent human rights concerns, and skepticism about the sincerity of denuclearization efforts. His regime is often scrutinized for its authoritarian practices and its impact on the well-being of the North Korean population. Stay informed on global leadership issues and ethical governance at johnchen.net.
- International Sanctions: North Korea faces numerous international sanctions due to its nuclear and missile programs, impacting its economy and international relations.
- Human Rights Concerns: Kim’s regime is frequently criticized for human rights abuses, including political repression and severe restrictions on freedom.
- Denuclearization Skepticism: Despite pledges, there is widespread skepticism about the sincerity and effectiveness of North Korea’s denuclearization efforts.
11. How Does Kim Jong Un Maintain Control Over North Korea?
Kim Jong Un maintains control over North Korea through strict surveillance, propaganda, and suppression of dissent, ensuring loyalty and compliance. Kim Jong Un maintains tight control over North Korea through a combination of strict surveillance, pervasive propaganda, and the suppression of dissent. These methods ensure loyalty and compliance among the population, reinforcing his authoritarian rule. The regime’s grip on information and its ability to control narratives are key to maintaining stability. Explore strategies for leadership and control in different contexts at johnchen.net.
- Surveillance: The government closely monitors its citizens, restricting their movement, communication, and access to information.
- Propaganda: State-controlled media disseminates propaganda that glorifies Kim Jong Un and the regime, reinforcing their authority.
- Suppression of Dissent: Any form of dissent is quickly and harshly suppressed, discouraging opposition and maintaining control.
12. What Role Does the Military Play Under Kim Jong Un’s Leadership?
The military is central to Kim Jong Un’s power, receiving significant resources and playing a key role in enforcing state policies. The military holds a pivotal role under Kim Jong Un, receiving substantial resources and playing a key part in enforcing state policies. It serves not only as a defense force but also as a symbol of national strength and a tool for internal control. The military’s loyalty to Kim Jong Un is crucial for maintaining his grip on power. Learn more about the dynamics between leadership and military power at johnchen.net.
- Resource Allocation: A significant portion of the national budget is allocated to the military, reflecting its importance to the regime.
- Enforcement of Policies: The military is involved in enforcing state policies and maintaining order within North Korea.
- Loyalty: The military’s unwavering loyalty to Kim Jong Un is essential for his continued rule.
13. How Does Kim Jong Un’s Leadership Impact the North Korean Economy?
Kim Jong Un’s economic policies, including a focus on self-reliance, have led to both challenges and limited improvements in some sectors. Kim Jong Un’s economic policies have aimed at self-reliance, leading to both challenges and limited improvements in some sectors. Despite international sanctions, the regime has attempted to boost domestic production and improve living standards, with varying degrees of success. The focus on economic development alongside military strength remains a central tenet of his leadership. Gain insights on economic leadership at johnchen.net.
- Self-Reliance (Juche): The regime emphasizes self-reliance, aiming to reduce dependence on foreign aid and trade.
- Limited Improvements: Some sectors have seen modest improvements, but overall economic growth remains constrained by sanctions and internal challenges.
- Economic Development Focus: Kim Jong Un has stressed the importance of economic development alongside military strength, balancing these priorities.
14. What is Kim Jong Un’s Relationship with China?
Kim Jong Un’s relationship with China is complex, marked by economic ties and diplomatic support, but also strains over North Korea’s nuclear ambitions. The relationship between Kim Jong Un and China is complex, characterized by economic ties and diplomatic support, alongside strains due to North Korea’s nuclear ambitions. China remains a crucial ally and trading partner, but also urges denuclearization. Understanding this dynamic is essential for grasping the geopolitical landscape in the region. Learn about complex international relationships at johnchen.net.
- Economic Ties: China is North Korea’s largest trading partner, providing essential economic support.
- Diplomatic Support: China has often provided diplomatic support to North Korea, advocating for dialogue and peaceful resolution of conflicts.
- Tensions over Nuclear Program: China has expressed concerns and disapproval of North Korea’s nuclear program, urging denuclearization and adherence to international norms.
15. How Does Kim Jong Un Use Propaganda and Media Control?
Kim Jong Un uses propaganda and strict media control to cultivate a cult of personality and maintain ideological conformity. Kim Jong Un utilizes propaganda and strict media control to cultivate a cult of personality and maintain ideological conformity. State-controlled media promotes an idealized image of Kim Jong Un, reinforcing his authority and suppressing dissenting voices. This control over information is critical to maintaining his grip on power. Discover how leaders shape public opinion at johnchen.net.
- Cult of Personality: Propaganda promotes an idealized image of Kim Jong Un, portraying him as a benevolent and infallible leader.
- Media Control: Strict censorship and control over all media outlets ensure that only state-approved information is disseminated.
- Ideological Conformity: Propaganda reinforces the regime’s ideology, suppressing dissenting voices and maintaining political control.
16. What Strategies Does Kim Jong Un Employ in International Negotiations?
Kim Jong Un employs a mix of brinkmanship, strategic concessions, and direct diplomacy to advance North Korea’s interests in international negotiations. Kim Jong Un employs a mix of brinkmanship, strategic concessions, and direct diplomacy to advance North Korea’s interests in international negotiations. He often uses a combination of assertive demands and unexpected gestures to influence discussions. Understanding these strategies provides insights into North Korea’s approach to global relations. Gain a deeper understanding of negotiation tactics at johnchen.net.
- Brinkmanship: Kim Jong Un uses assertive tactics, such as nuclear tests and missile launches, to gain leverage in negotiations.
- Strategic Concessions: He sometimes offers strategic concessions, such as halting nuclear tests, to create momentum and foster dialogue.
- Direct Diplomacy: Kim Jong Un has engaged in direct diplomacy with world leaders, including summits with the leaders of the United States and South Korea.
17. What Role Do Sanctions Play in Shaping Kim Jong Un’s Policies?
Sanctions significantly constrain North Korea’s economy, influencing Kim Jong Un’s policies by limiting resources and increasing the need for diplomatic engagement. Sanctions play a significant role in shaping Kim Jong Un’s policies by constraining North Korea’s economy. These restrictions limit available resources and increase the need for diplomatic engagement. Kim Jong Un navigates these challenges by focusing on self-reliance and seeking avenues to alleviate economic pressures. Explore the impact of economic policies on international relations at johnchen.net.
- Economic Constraints: Sanctions limit North Korea’s access to international markets, technology, and financial resources.
- Influence on Policies: The economic constraints influence Kim Jong Un’s policies by increasing the need for diplomatic engagement and self-reliance.
- Adaptation: Kim Jong Un has adapted to sanctions by focusing on domestic production and seeking ways to alleviate economic pressures.
18. How Does Kim Jong Un Balance Military and Economic Priorities?
Kim Jong Un balances military and economic priorities by pursuing parallel development, allocating resources to both sectors while emphasizing self-reliance. Kim Jong Un balances military and economic priorities through a strategy of parallel development, allocating resources to both sectors while emphasizing self-reliance. This approach aims to strengthen national defense while also improving the country’s economic conditions. The balance is often challenging, particularly given the constraints imposed by international sanctions. Learn about strategic leadership decisions at johnchen.net.
- Parallel Development: Kim Jong Un pursues a strategy of parallel development, focusing on both military and economic advancements.
- Resource Allocation: Resources are allocated to both sectors, reflecting the regime’s commitment to both national defense and economic progress.
- Challenges: Balancing these priorities is challenging, particularly given the constraints imposed by international sanctions and internal inefficiencies.
19. How Does Kim Jong Un Address Internal Dissent?
Kim Jong Un addresses internal dissent through strict surveillance, suppression of opposition, and ideological indoctrination, maintaining tight control over the population. Kim Jong Un addresses internal dissent through strict surveillance, suppression of opposition, and ideological indoctrination. These methods maintain tight control over the population and prevent any organized resistance. The regime’s ability to monitor and control its citizens is central to maintaining stability. Gain insights into authoritarian leadership at johnchen.net.
- Strict Surveillance: The government monitors its citizens closely, restricting their freedom of movement, communication, and access to information.
- Suppression of Opposition: Any form of dissent is quickly and harshly suppressed, discouraging opposition and maintaining control.
- Ideological Indoctrination: Propaganda and education reinforce the regime’s ideology, suppressing dissenting voices and ensuring political conformity.
20. What is Kim Jong Un’s Vision for North Korea’s Future?
Kim Jong Un’s vision for North Korea involves a strong, self-reliant nation with advanced military capabilities and improved economic conditions, though the path to achieving this remains uncertain. Kim Jong Un envisions a strong, self-reliant North Korea with advanced military capabilities and improved economic conditions. While the path to achieving this vision remains uncertain, his leadership continues to shape the country’s trajectory. Stay informed on global leadership perspectives at johnchen.net.
- Strong and Self-Reliant Nation: Kim Jong Un aims to build a strong and self-reliant nation, reducing dependence on foreign aid and trade.
- Advanced Military Capabilities: He seeks to maintain and enhance North Korea’s military strength, particularly its nuclear and missile programs.
- Improved Economic Conditions: Kim Jong Un has emphasized the importance of improving the country’s economic conditions and raising living standards.
21. What are the Key Elements of Kim Jong Un’s Leadership Style?
Kim Jong Un’s leadership style combines authoritarian control, strategic decision-making, and a public image of strength and decisiveness. Kim Jong Un’s leadership style blends authoritarian control, strategic decision-making, and a public image of strength and decisiveness. These elements shape his approach to governing North Korea and navigating international relations. Understanding his leadership style is crucial for interpreting his actions and predicting future policies. Discover different leadership styles at johnchen.net.
- Authoritarian Control: Kim Jong Un maintains tight control over the government, military, and population, ensuring loyalty and compliance.
- Strategic Decision-Making: He makes strategic decisions aimed at advancing North Korea’s interests, often balancing competing priorities.
- Public Image: Kim Jong Un cultivates a public image of strength and decisiveness, reinforcing his authority and projecting confidence.
22. How Does Kim Jong Un Handle Relationships with Other World Leaders?
Kim Jong Un handles relationships with other world leaders through a mix of diplomacy, assertiveness, and strategic engagement, adapting his approach to different contexts. Kim Jong Un manages relationships with other world leaders through a mix of diplomacy, assertiveness, and strategic engagement. He adapts his approach based on the context and the specific goals he aims to achieve. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping North Korea’s international relations. Gain insights on international diplomacy at johnchen.net.
- Diplomacy: Kim Jong Un engages in diplomatic dialogue with other world leaders, seeking to build relationships and address mutual concerns.
- Assertiveness: He asserts North Korea’s interests and positions, often using a combination of diplomacy and pressure tactics.
- Strategic Engagement: Kim Jong Un strategically engages with other countries, forming alliances and partnerships to advance North Korea’s goals.
23. What Impact Does Kim Jong Un’s Health Have on North Korea’s Stability?
Kim Jong Un’s health is a significant factor in North Korea’s stability, as any uncertainty about his well-being could lead to political instability and succession questions. Kim Jong Un’s health is a significant factor in North Korea’s stability, as any uncertainty about his well-being could lead to political instability and succession questions. Given the centralized nature of power in North Korea, concerns about his health have far-reaching implications. Stay informed on geopolitical stability at johnchen.net.
- Political Instability: Uncertainty about Kim Jong Un’s health could trigger political instability and power struggles within North Korea.
- Succession Questions: Questions about succession would arise, potentially leading to uncertainty and instability.
- Centralized Power: Given the centralized nature of power in North Korea, his health has far-reaching implications for the country’s leadership and direction.
24. How Does Kim Jong Un Utilize Cultural Events to Promote His Leadership?
Kim Jong Un utilizes cultural events to promote his leadership by showcasing national unity and reinforcing his image as a benevolent leader. Kim Jong Un utilizes cultural events to promote his leadership by showcasing national unity and reinforcing his image as a benevolent leader. These events provide opportunities to glorify his achievements and strengthen his cult of personality. Discover how cultural events can shape leadership perceptions at johnchen.net.
- Showcasing National Unity: Cultural events are used to demonstrate national unity and support for the regime.
- Reinforcing Leadership Image: These events reinforce Kim Jong Un’s image as a strong and caring leader.
- Glorifying Achievements: Cultural events provide opportunities to glorify his achievements and strengthen his cult of personality.
25. What Role Does Kim Yo Jong Play in Kim Jong Un’s Administration?
Kim Yo Jong plays a significant role in Kim Jong Un’s administration as a key advisor, diplomat, and potential successor, wielding considerable influence. Kim Yo Jong plays a significant role in Kim Jong Un’s administration as a key advisor, diplomat, and potential successor, wielding considerable influence. Her involvement in high-level meetings and diplomatic missions underscores her importance within the regime. Learn more about the roles of key advisors in leadership at johnchen.net.
- Key Advisor: Kim Yo Jong serves as a trusted advisor to Kim Jong Un, providing guidance on policy and strategy.
- Diplomat: She has represented North Korea in diplomatic missions, engaging with world leaders and fostering international relations.
- Potential Successor: Kim Yo Jong is seen as a potential successor to Kim Jong Un, positioning her as a key figure in the future of North Korea.
26. How Does Kim Jong Un’s Approach to Technology Affect North Korea?
Kim Jong Un’s approach to technology involves selective adoption, emphasizing military applications while restricting access for the general population. Kim Jong Un’s approach to technology involves selective adoption, emphasizing military applications while restricting access for the general population. This approach strengthens North Korea’s defense capabilities while maintaining control over information. Stay informed on technology and leadership at johnchen.net.
- Military Applications: Kim Jong Un prioritizes the development and use of technology for military purposes, enhancing North Korea’s defense capabilities.
- Restricted Access: Access to technology is restricted for the general population, maintaining control over information and preventing dissent.
- Selective Adoption: Kim Jong Un selectively adopts technologies that support the regime’s goals, while limiting broader access.
27. What Efforts Has Kim Jong Un Made to Improve North Korea’s International Image?
Kim Jong Un has made efforts to improve North Korea’s international image through diplomatic engagements, cultural exchanges, and selective media portrayals. Kim Jong Un has made efforts to improve North Korea’s international image through diplomatic engagements, cultural exchanges, and selective media portrayals. These efforts aim to present a more positive image of the country and foster better relationships with the international community. Discover how leaders manage public perception at johnchen.net.
- Diplomatic Engagements: Kim Jong Un has engaged in diplomatic dialogue with world leaders, seeking to build relationships and address mutual concerns.
- Cultural Exchanges: Cultural exchanges promote a more positive image of North Korea, fostering better understanding and goodwill.
- Selective Media Portrayals: State-controlled media selectively portrays North Korea in a positive light, highlighting achievements and downplaying challenges.
28. How Does Kim Jong Un’s Economic Policy Compare to His Father’s?
Kim Jong Un’s economic policy differs from his father’s by incorporating limited market-oriented reforms while maintaining state control. Kim Jong Un’s economic policy differs from his father’s by incorporating limited market-oriented reforms while maintaining state control. This approach aims to improve economic efficiency while preserving the regime’s authority. Explore economic policies and their impact at johnchen.net.
- Limited Market-Oriented Reforms: Kim Jong Un has introduced limited market-oriented reforms, such as allowing some private enterprise and agricultural reforms.
- State Control: The state maintains control over key sectors of the economy, ensuring the regime’s authority and preventing significant shifts in power.
- Economic Efficiency: The reforms aim to improve economic efficiency and productivity while preserving the regime’s control.
29. What Impact Does Kim Jong Un’s Nuclear Ambitions Have on Regional Security?
Kim Jong Un’s nuclear ambitions significantly destabilize regional security, leading to increased tensions and military build-ups in the region. Kim Jong Un’s nuclear ambitions significantly destabilize regional security, leading to increased tensions and military build-ups in the region. Neighboring countries and international powers respond with heightened vigilance and strategic countermeasures. Stay informed on geopolitical security issues at johnchen.net.
- Increased Tensions: North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs escalate tensions in the region, raising the risk of military conflict.
- Military Build-Ups: Neighboring countries and international powers respond with heightened vigilance and strategic countermeasures, leading to military build-ups.
- Regional Instability: Kim Jong Un’s nuclear ambitions contribute to overall regional instability, posing a significant threat to peace and security.
30. How Does Kim Jong Un Use Ideology to Maintain Power?
Kim Jong Un uses ideology to maintain power by promoting Juche (self-reliance) and loyalty to the Kim dynasty, reinforcing his authority and suppressing dissent. Kim Jong Un uses ideology to maintain power by promoting Juche (self-reliance) and loyalty to the Kim dynasty, reinforcing his authority and suppressing dissent. This ideological framework helps legitimize his rule and maintain social control. Discover the power of ideology in leadership at johnchen.net.
- Juche (Self-Reliance): The ideology of Juche emphasizes self-reliance, reducing dependence on foreign aid and trade and promoting national pride.
- Loyalty to the Kim Dynasty: Propaganda and education reinforce loyalty to the Kim dynasty, portraying Kim Jong Un as the rightful leader.
- Suppression of Dissent: Ideological conformity suppresses dissenting voices and maintains political control, ensuring the regime’s stability.
Want to understand more about Kim Jong Un’s leadership and its impact on global affairs? Visit johnchen.net for in-depth analysis and exclusive content. Explore articles, interviews, and insights from experts that can help you stay informed and gain a deeper understanding of leadership and international relations.
Address: [Địa chỉ văn phòng hoặc địa chỉ liên hệ của John Chen nếu có]
Phone: +1 (415) 555-0100
Website: johnchen.net
FAQ About Kim Jong Un
1. What is Kim Jong Un known for?
Kim Jong Un is known for being the supreme leader of North Korea, his aggressive pursuit of nuclear weapons, and his complex relationships with world leaders.
2. How did Kim Jong Un become the leader of North Korea?
Kim Jong Un became the leader of North Korea after his father, Kim Jong Il, died in December 2011.
3. What is Kim Jong Un’s policy of “Byungjin”?
“Byungjin” is a policy of parallel development, focusing on both economic development and strengthening military capabilities.
4. What was the outcome of the summits between Kim Jong Un and Donald Trump?
The summits resulted in initial pledges towards denuclearization but did not lead to a comprehensive agreement.
5. What are some of the challenges Kim Jong Un faces as a leader?
Challenges include international sanctions, human rights concerns, and skepticism about denuclearization efforts.
6. How does Kim Jong Un maintain control over North Korea?
Kim Jong Un maintains control through strict surveillance, propaganda, and suppression of dissent.
7. What role does the military play under Kim Jong Un’s leadership?
The military is central to Kim Jong Un’s power, receiving significant resources and playing a key role in enforcing state policies.
8. What are Kim Jong Un’s economic policies for North Korea?
Kim Jong Un’s economic policies include self-reliance and limited market-oriented reforms while maintaining state control.
9. How does Kim Jong Un utilize propaganda in North Korea?
Kim Jong Un uses propaganda to cultivate a cult of personality and maintain ideological conformity.
10. What is Kim Yo Jong’s role in Kim Jong Un’s administration?
Kim Yo Jong is a key advisor, diplomat, and potential successor, wielding considerable influence.

